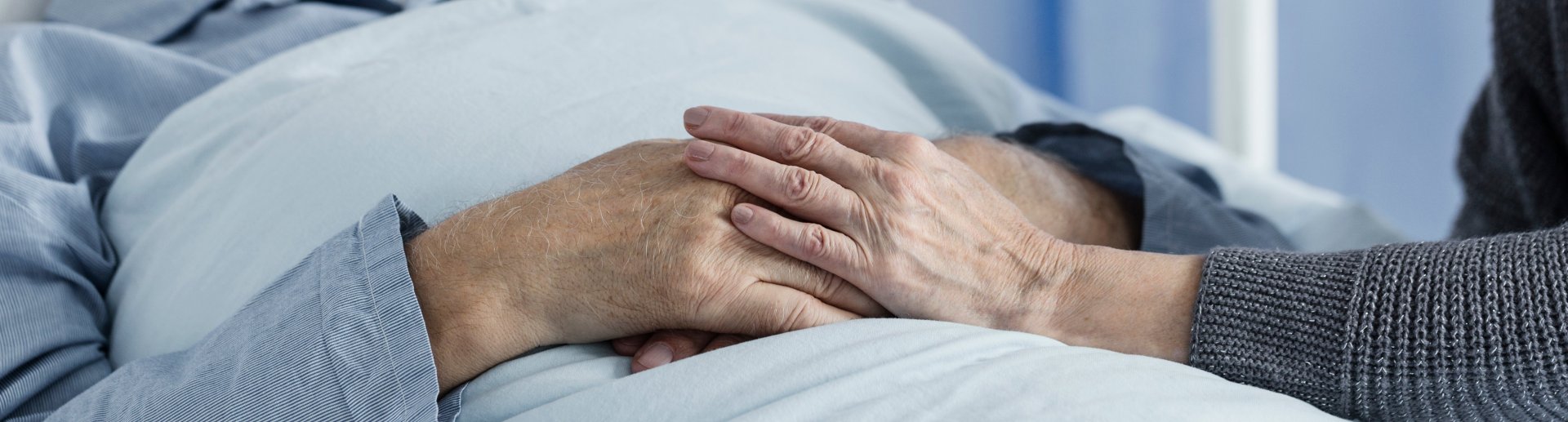
We support patient autonomy and work to protect patients from the imposition of other people's personal religious views.
There is widespread support amongst the public for a compassionate law that permits assisted dying under certain circumstances.
But religious lobbying exerts a disproportionate influence on the debate on assisted dying, frustrating much-needed reform.
Assisted dying (AD) is when a person chooses to be given help to die, usually because they are terminally ill and suffering unbearably.
AD is legal in a growing number of countries around the world. In all these jurisdictions there are strict guidelines and safeguards to ensure AD is not misused. Where AD is an option, it complements palliative care rather than replacing it.
AD is not explicitly legal anywhere in the UK. Terminally ill people who wish to end their suffering more quickly have very few options.
Travelling to a country where their death can be assisted legally isn't a viable option for most, due to the high expense and the difficulties in travelling with a terminal illness. What's more, friends and relatives who accompany or help someone travel abroad for AD may be prosecuted.
Terminally ill people in the UK may therefore resort to taking their own life, leading to botched suicides, or asking the help of loved ones. This puts friends and relatives in a horrendous position: either they must watch their loved one suffer, or they must help them die and risk jail in the process.
The largest poll ever conducted on assisted dying found 84% of people in Britain support a change in the law. This includes 82% of Christians and 90% of nonreligious people.
Many regard refusing people a final relief from unbearable suffering as a harmful act. But strong opposition to AD comes from religious leaders who think AD goes against the will of their gods.
We support the democratic right of all people to contribute to the debate on AD. But policy decisions should be guided by evidence, compassion and respect for the principle of patient autonomy, rather than religious dogma. The views of the general public, professionals and relevant organisations should be fairly reflected at policy level.
Within the National Secular Society, individual members hold a range of views about AD. All are agreed that religious privilege should have no place in the decision-making process.
Take action!
1. Write to your MP
Ask your MP to support properly regulated assisted dying.
2. Share your story
Tell us why you support this campaign, and how you are personally affected by the issue. You can also let us know if you would like assistance with a particular issue.
3. Join the National Secular Society
Become a member of the National Secular Society today! Together, we can separate religion and state for greater freedom and fairness.
Latest updates
Doctors’ union drops opposition to assisted dying
Posted: Tue, 14 Sep 2021 15:23
A doctors' union has dropped its opposition to assisted dying in a historic vote.
The British Medical Association (BMA), which represents about 150,000 medics, today voted to adopt a position of neutrality on physician-assisted dying at its annual representative meeting.
The change comes ahead of the second reading of the Assisted Dying Bill due later this year. The bill would legalise assisted dying as a choice for terminally ill, mentally competent adults in their final months of life.
BMA member views
In a survey of BMA members last year, only one third of respondents expressed support for the BMA's position of active opposition to assisted dying. Half were in favour of its legalisation.
Speaking in support of the motion at the meeting, chair of the National Secular Society's Secular Medical Forum, Dr Antony Lempert, told delegates that the switch to a neutral position "does not seek to silence minority voices" and would enable the BMA to "share the wide spectrum of members' opinion, expertise and concerns."
He said doctors' primary responsibility was to patients, "the vast majority of whom deplore the criminalisation of any attempt by loving relatives or by doctors to help desperate people to escape the torment of unbearable suffering".
Voting results
Forty-nine per cent of voters supported the change.
The BMA said it will "neither support nor oppose attempts to change the law" on assisted dying.
However, it said it "will not be silent on this issue" as it has a "responsibility to represent our members' interests and concerns in any future legislative proposals".
Dr Lempert welcomed the outcome of the vote. He said: "Today's vote more fairly reflects the broad range of opinions of BMA members and moves much closer to representing the views of the public who are largely in favour of decriminalisation of assisted dying.
"With its new policy of neutrality, the BMA can now engage fully with any legal developments and will no longer be able to suggest that doctors are against assisted dying which is demonstrably untrue."
Notes
- In 2019 the Royal College of Physicians also adopted a neutral stance on the issue.
- The largest poll ever conducted on assisted dying found 84% people in Great Britain support a change in the law. This includes 82% Christians and 90% nonreligious people.
Listen to our recent podcast with Molly Meacher and AC Grayling on the Assisted Dying Bill.
Read more: The BMA's opportunity to rethink its position on assisted dying
Image by Darko Stojanovic from Pixabay
Religious privilege causing injustice, NSS tells Law Commission
Posted: Wed, 4 Aug 2021 14:23
The National Secular Society has argued that religious privilege creates inconsistencies and unfairness in laws on education, charity, health and animal welfare in response to a consultation.
The NSS has submitted evidence on these issues to the Law Commission, which has sought views on what should be included in its latest programme of recommended legal reforms.
The commission is a statutory independent body that keeps the law of England and Wales under review and recommends reform where it judges that it's needed.
NSS recommendations
The NSS said the commission should consider:
- Laws requiring collective worship in schools.
- The provision in charity law which makes 'the advancement of religion' a charitable purpose in its own right.
- The lack of effective protection for boys in laws on genital cutting.
- The religious exemption to animal welfare laws that allows non-stun slaughter.
- Assisted dying law.
Law on collective worship
Sections 70 and 71 of the School Standards and Framework Act 1998 require that all state-funded schools in England and Wales "shall on each school day take part in an act of collective worship".
Even in schools with no religious designation, the worship must be "wholly or mainly of a Christian character".
The NSS's submission said this law was incompatible with human rights laws and the principle of equality, and opened the door to inappropriate external evangelism in schools.
Charity law
In laws on charity throughout the UK, 'the advancement of religion' is a recognised charitable purpose in its own right.
The NSS's submission said removing this would ensure greater fairness and mitigate the damage that harmful religious organisations cause.
The NSS made the case for removing 'the advancement of religion' as a charitable purpose in a report, For the Public Benefit?, published in 2019.
Religious organisations would still be able to register for charitable status under another recognised charitable purpose, as many already do.
Genital cutting
The NSS's submission called on the commission to consider the disparity between the protections afforded to boys and girls regarding autonomy over their genitals.
It noted that boys are not given explicit protection from non-consensual, medically unnecessary circumcision or other modifications to their genitals.
It said this was incompatible with human rights law and left many at risk of serious harm.
Animal welfare
The society highlighted the religious exemption from animal welfare laws that allows animals to be slaughtered without stunning according to Jewish and Muslim rites.
There is widespread consensus among veterinary and animal welfare groups that it's more humane to stun an animal before slaughter than not to do so.
The NSS argues for the repeal of the religious exemption, and for the labelling of meat from animals subject to non-stun slaughter while the exemption remains in place.
Assisted dying law
The NSS also called on the commission to draft a legal framework for assisted dying, to guide potential legislation.
The society said a disproportionate level of influence is granted to religious groups in debates on assisted dying, and argued that the views of the general public, professionals and relevant organisations should be fairly reflected at policy level.
It said a framework could help to guide the government into formulating compassionate and safe legislation to allow for assisted dying under certain circumstances.
NSS comment
NSS head of policy and research Megan Manson said: "Our reforms identify several significant ways in which religious privilege within the law causes inequality, injustice and harm.
"Deference to religion has helped to create outdated, unfair and often unnecessarily complex laws in these areas. We hope the Law Commission will consider our recommendations as it outlines its next programme for reform."
About the Law Commission's review
- The Law Commission undertakes a public consultation every few years, with a view to submitting a draft programme of law reform to the lord chancellor.
- This is the commission's 14th programme of reform. The 13th was submitted in late 2017.
Image: Jarretera / Shutterstock.com.